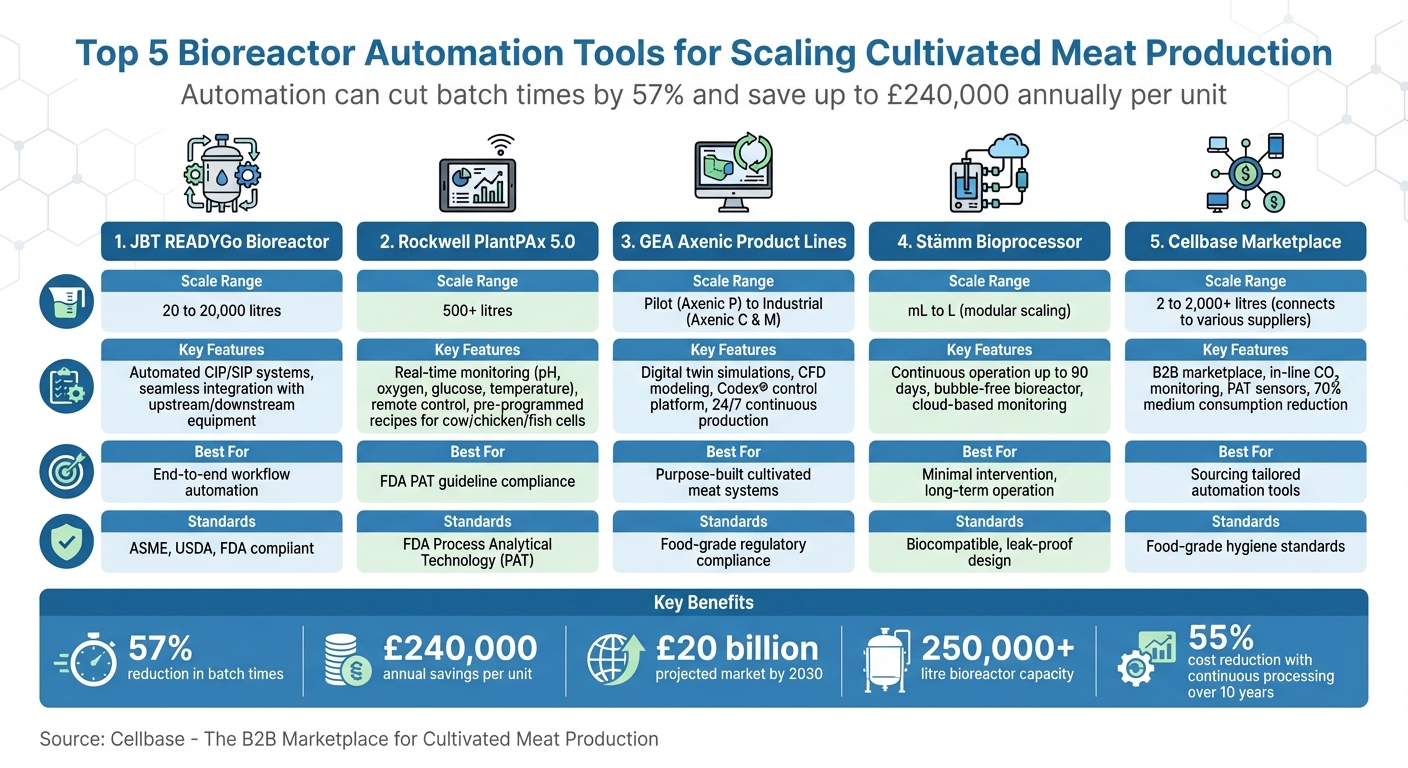
Scaling cultivated meat production requires precise automation to manage complex biological processes, ensure consistency, and reduce costs. Automation can cut batch times by 57%, improve efficiency, and save up to £240,000 annually per unit. With bioreactors exceeding 250,000 litres, manual processes are no longer viable. Here's a quick look at the top tools driving this transformation:
- JBT READYGo Bioreactor: Scales from 20 to 20,000 litres, integrates with existing systems, and features automated cleaning and sterilisation.
- Rockwell PlantPAx 5.0: Supports bioreactors over 500 litres with real-time monitoring, remote control, and pre-programmed recipes.
- GEA Axenic Product Lines: Purpose-built for cultivated meat, using digital simulations to optimise large-scale production.
- Stämm Bioprocessor: Modular, continuous system for long-term operation with minimal intervention.
- Cellbase Marketplace: Connects buyers with suppliers for tailored automation tools and sensors for bioreactors.
Automation ensures precise control over variables like pH, oxygen, and nutrient distribution, enabling large-scale, cost-efficient production. Below, we dive into how these tools are shaping the future of cultivated meat manufacturing.
Top 5 Bioreactor Automation Tools for Cultivated Meat Production Comparison
1. JBT Corporation's READYGo Bioreactor
Scalability for Commercial Cultivated Meat Production
The READYGo bioreactor is built to bridge the gap between lab-scale experiments and full-scale commercial production of cultivated meat. It offers working volumes ranging from 20 litres for pilot projects to an impressive 20,000 litres for large-scale operations. This ensures that producers can maintain consistent bioprocess parameters as they scale up. With years of industry expertise and efficient sanitary process piping, JBT helps reduce lead times and capital costs - key factors as the cultivated meat sector is predicted to grow to £20 billion by 2030 [4].
"We view the success of the cultivated meat market as critical to meeting global protein demand." – Carlos Fernandez, Executive Vice President of Customer Sustainability and Market Development [4]
The platform's scalability is further supported by advanced automation systems that simplify the entire production process.
Automation Features for Streamlined Production
The READYGo bioreactor incorporates digital Clean-in-Place (CIP) and Sterilisation-in-Place (SIP) systems, which uphold rigorous hygiene and media sterility standards while cutting down on manual intervention. It seamlessly connects with upstream and downstream equipment - such as media preparation units, harvest/hold systems, and protein packaging lines - offering a fully automated, end-to-end workflow. Designed to be user-friendly, the system is manageable by standard manufacturing staff, eliminating the need for highly specialised operators. Additionally, factory acceptance testing (FAT) by certified engineers ensures quicker installation and commissioning of cell culture facilities.
"We designed this platform specifically to allow customisation and tailoring of the features based on a client's specific requirements for cultivated meat products." – Dave Mitchell, Product Line Director of Pharma and Life Sciences at JBT [2]
Ease of Integration with Existing Infrastructure
In addition to its automation capabilities, the READYGo bioreactor is designed for seamless integration with both existing in-house systems and third-party components. Its adaptability allows it to function smoothly within JBT's own equipment ecosystem or alongside equipment from other suppliers.
"We are doing so in a way that not only integrates into the customer's preferred component suppliers' current system, but we provide expert recommendations when necessary." – Schoen Paschka, Director of Sales & Marketing, A&B Process Systems [4]
Developed in partnership with CRB, the bioreactor is engineered to comply with ASME, USDA, and FDA standards. It meets global bioprocessing requirements while ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure, making it a reliable choice for cultivated meat production [2].
sbb-itb-ffee270
Design, Characterization, and Scale-Up Strategy for a New Single-Use Production-Scale Bioreactor
2. Rockwell's PlantPAx 5.0 System

Building on the momentum of JBT Corporation's READYGo, Rockwell's PlantPAx 5.0 System is another advanced option for scaling up cultivated meat production.
Scalability for Commercial Cultivated Meat Production
The PlantPAx 5.0 System is designed to support the transition to large-scale bioreactors, often exceeding 500 litres. At this scale, ensuring consistent product quality becomes a significant challenge, and advanced automation plays a vital role in addressing it [5]. The system enables real-time monitoring of key process parameters such as pH, dissolved oxygen, glucose levels, temperature, and biomass. This level of precision aligns with FDA Process Analytical Technology (PAT) guidelines, helping manufacturers maintain control over bioprocesses [3]. By supporting continuous or perfusion methods instead of traditional batch processing, the system boosts production throughput, making it a practical solution for commercial operations.
Automation Features for Streamlined Production
The PlantPAx 5.0 System incorporates advanced control features to replicate the ideal conditions for cell growth. It carefully manages variables like temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, and nutrient supply to create an environment that mimics natural biological processes [2]. One standout feature is its remote monitoring capability, which allows operators to oversee production and adjust parameters without being physically present. This not only improves efficiency but also simplifies data management. Additionally, the system comes with pre-programmed recipes tailored for cultivating cow, chicken, and fish cells, removing the need to develop custom protocols and speeding up production processes [2].
3. GEA Axenic Product Lines
GEA's Axenic product lines bring together tools that simplify production and ensure consistent results, making large-scale cultivated meat production more achievable.
The Axenic portfolio includes three distinct product lines: Axenic P (Pilot), Axenic C (Cell Culture/Industrial), and Axenic M (Microbial/Industrial) [6][9]. Unlike pharmaceutical bioreactors that are retrofitted for food production, these systems are purpose-built for cultivated meat, ensuring they meet all regulatory standards [6].
By incorporating advanced automation technologies, the Axenic systems provide scalable solutions tailored to the specific challenges of commercial cultivated meat production.
Scalability for Commercial Cultivated Meat Production
Scaling cultivated meat production comes with unique challenges, particularly understanding how cells behave when moving from small lab setups to industrial volumes. GEA tackles this with digital twin simulations and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to model factors like oxygen transfer, shear forces, and temperature gradients at large scales, even before equipment is installed [6][9]. This virtual testing helps identify potential problems - such as uneven media distribution or excessive shear stress on delicate cells - before significant investments are made.
"The Axenic® P accurately recapitulates conditions in factory units, including our Axenic® C and Axenic® M bioreactors, to generate actionable insight on how key factors... impact on cell health, process stability and, ultimately, yield." - GEA [9]
The Axenic C bioreactor is specifically designed for mammalian and eukaryotic cells. It features multiple gas connections to precisely control oxygen and carbon dioxide levels across large volumes [6]. This is crucial for cultivated meat, where different cell types - from delicate embryonic cells to sturdier muscle cells - require customised shear force management to maximise output during scale-up [6].
Automation Features for Streamlined Production
GEA's Codex® process control platform acts as the automation hub for all Axenic systems, offering centralised recipe management and real-time monitoring [6][8]. Its valve feedback systems immediately detect and report failures, helping to prevent contamination and minimise batch losses. Automated sterile barriers on media and harvest lines allow for continuous 24/7 production cycles without the need for manual intervention [6][8].
The Axenic P system features split-range control, which independently manages oxygen delivery and agitator speeds. This ensures energy efficiency by choosing the most economical gas delivery method while maintaining optimal conditions for cell growth [9]. Meanwhile, the GEA Codex® Historian logs all process data, ensuring consistent results across batches - a necessity for large-scale production [6].
Ease of Integration with Existing Infrastructure
GEA begins with a design study to ensure the Axenic system integrates smoothly with existing equipment, including media tanks and harvest lines [6][8]. The Axenic P pilot system is particularly adaptable, featuring replaceable hoses and multiple inlets/outlets for easy connection to facility infrastructure [9].
"We like to start with a basic design study to go through your process, what you do today, and evaluate the process with you to make sure that your new facility will fit together with equipment up and downstream of the bioreactors." - GEA [6]
The GEA Codex platform ensures a seamless transition from pilot to industrial scales, allowing producers to transfer process data, sensors, and recipes directly from Axenic P to Axenic C systems without the need for reconfiguration [9]. This continuity significantly reduces the risks and costs associated with scaling up. With over two decades of experience in modular bioreactor design, GEA also offers interchangeable components, such as agitator impellers, enabling hardware adjustments for different processes or applications [7][9].
4. Stämm's Automated Continuous Bioreactor (Bioprocessor)

Stämm's Bioprocessor transforms traditional batch processes into a continuous, automated system capable of running for up to 90 days with minimal human involvement. This setup not only increases production efficiency but also cuts down on labour costs and inconsistencies [10]. Let’s dive into its specialised modules and integrated control systems that make this possible.
Scalability for Commercial Cultivated Meat Production
The Bioprocessor is built with a modular "plug & play" design, featuring three key modules - Inoculation, Production, and Harvest. These modules work together to maintain a steady production flow, allowing seamless scaling from small millilitre-scale lab trials to litre-scale commercial manufacturing without overhauling the core process [10].
"Consistently scaling from mL to L, from lab trials to commercial & industrial use." – Stämm [10]
At the centre of the system lies the Bubble-free Bioreactor (BfB). This component uses microvascular channels made from biocompatible resin to maintain a laminar flow environment free from stress. The design ensures leak-proof, gas-permeable conditions, eliminating the need for traditional filters and simplifying operations [10].
Automation Features for Streamlined Production
The system is designed to streamline production through automation:
- The Inoculation Module handles the continuous inflow of cells automatically.
- The sealed Production Module self-regulates environmental conditions to optimise growth.
- The Harvest Module integrates cell counting and sampling to ensure optimal output before downstream processing.
All these processes are managed via a cloud-based Biomanufacturing App, which provides real-time monitoring, data collection, and automated maintenance across various production sites [10].
Ease of Integration with Existing Infrastructure
The modular design supports both suspension and adherent cultures, making it adaptable to existing facilities. Its cloud-based management system simplifies integration, allowing producers to monitor and standardise critical parameters across multiple production locations [10].
"Effortlessly scale up biologics and cell therapies with our plug & play continuous bioreactor." – Stämm [10]
This cloud system ensures consistency and efficiency, regardless of where the production takes place, offering a unified approach to biomanufacturing [10].
5. Cellbase for Sourcing Bioreactor Automation Tools
Cellbase stands out as the first specialised B2B marketplace created exclusively for the cultivated meat industry. Unlike hardware-specific tools or general platforms, it connects production managers and procurement teams with a network of verified suppliers. These suppliers provide bioreactor automation tools, sensors, and control systems tailored to the demands of cultivated meat production. By focusing on this niche, Cellbase ensures that every tool available aligns with the unique requirements of this field.
Tailored for Cultivated Meat Production
General lab supply platforms often fall short when it comes to the specific needs of cultivated meat. Cellbase, however, is designed with those needs in mind. The tools listed are optimised for animal cell culture, addressing challenges like preventing CO₂ build-up and improving medium recycling. Additionally, these tools meet food-grade hygiene standards, ensuring sterility and cost-effective medium use - both critical for scaling operations in this industry.
Supporting Commercial Scalability
Cellbase connects users with suppliers offering automation systems that can scale from small 2-litre setups to industrial-scale 2,000-litre operations. These systems feature advanced capabilities such as in-line CO₂ monitoring and automated feedback loops, which help maintain cell viability while cutting medium consumption by up to 70% [11].
Advanced Automation for Efficient Production
Through Cellbase, producers gain access to cutting-edge process analytical technology (PAT). These systems include in-line sensors for monitoring key parameters like viable cell density, pH, dissolved oxygen, and CO₂ levels. Real-time feedback loops automate nutrient and gas adjustments, ensuring optimal conditions for cell growth. Some suppliers even offer tools like Hamilton's Incyte sensor, which links permittivity data to meat texture - providing insights specifically tailored to cultivated meat production.
Seamless Integration with Existing Systems
Cellbase also simplifies the integration of new automation systems into existing production setups. Many of the listed tools are compatible with widely used control platforms like PlantPAx or DeltaV, making retrofitting straightforward. The platform offers technical support for system integration and calibration, ensuring new sensors and tools work seamlessly with both single-use and stainless-steel bioreactors. For added convenience, production teams can access guidance from dedicated Cell Ag Experts, helping them navigate complex automation needs with confidence.
How Cellbase Supports Scaling in Cultivated Meat Production
Scaling up cultivated meat production requires cutting-edge automation tools and a streamlined procurement process that connects buyers with reliable suppliers. Cellbase tackles this need as the world's first B2B marketplace exclusively focused on the cultivated meat industry [5]. By regularly updating its inventory, Cellbase ensures production managers can access the latest technologies tailored specifically for cultivated meat manufacturing.
One standout feature is the "Production Bioreactors" collection, which includes systems typically exceeding 500 litres - perfect for large-scale operations. These bioreactors come equipped with essential features like CIP (clean-in-place), SIP (sterilise-in-place), automated harvesting, and data management tools to support regulatory traceability. This specialised inventory is designed to meet the demands of commercial-scale cultivated meat production.
In addition to hardware, Cellbase offers access to Cell Ag Experts who help companies navigate technical sourcing challenges. Whether it’s integrating new automation systems with existing setups or selecting the best monitoring technologies, this guidance is invaluable. The platform also simplifies logistics with transparent pricing, quick checkout, and global cold chain shipping, making it easier for production teams to focus on scaling without logistical headaches.
For tools not already listed, Cellbase provides a sourcing form to onboard new suppliers, ensuring access to emerging technologies such as AI-driven biosensors and advanced in-line analytics. This adaptability means production teams can stay ahead of the curve, all through a single trusted platform. To further support scaling efforts, Cellbase’s Insights & News section offers updates on best practices, including sensor integration, bioreactor sterility testing, and ISO 14644 cleanroom monitoring standards.
Conclusion
Effective automation plays a central role in scaling and streamlining cultivated meat production. Choosing the right bioreactor automation tools means balancing scalability, automation capabilities, and specific industry requirements. Systems with open architecture and vessel-agnostic designs allow you to repurpose existing equipment while maintaining consistent operations from the lab to full-scale production [1]. This approach not only avoids vendor lock-in but also ensures your technology can adapt as production needs change.
For commercial success, automation paired with real-time monitoring is a must. By integrating Process Analytical Technology (PAT) ecosystems - like Raman analysers - batch times can be cut by 57%, delivering an annual return of £300,000 per unit [1]. Cloud-based platforms further lighten manual workloads, improving success rates and enabling high-density cultures that surpass 1×10⁷ cells/mL [3][12].
Economic modelling shows that continuous processing can reduce capital and operating costs by 55% over a decade compared to batch processing [3]. When selecting tools, it’s critical to focus on systems that support various bioprocess modes - batch, fed-batch, perfusion, and continuous - so you can maximise cell density while minimising downtime. Additionally, your automation setup must handle the oxygen transfer and heat dissipation challenges that come with large-scale production [3]. These benefits simplify the procurement process and set the stage for long-term growth.
Platforms like Cellbase help streamline procurement by connecting production teams with trusted suppliers of bioreactor automation tools tailored for cultivated meat. These platforms offer curated listings and expert advice, making it easier to navigate supplier networks and stay on top of new technological developments.
Finally, consider tools that can be deployed quickly - modern controllers can be operational within 12–16 weeks [1] - and those that support remote monitoring and seamless data integration across distributed control systems. This ensures your bioprocessing automation infrastructure scales effectively while meeting the rigorous food-grade standards essential for commercial cultivated meat production.
FAQs
How do I choose the right automation tool for my bioreactor scale?
To choose the best automation tool for your bioreactor scale in cultivated meat production, start by assessing your production stage and the type of bioreactor you're using, whether it's a stirred-tank or a perfusion system. Look for tools that offer advanced features such as AI capabilities, real-time monitoring, and sensor integration. These can help streamline scalability, minimise errors, and cut costs.
It's also crucial to ensure the tool is compatible with your existing equipment. Prioritise options that support scalability, have robust automation protocols, and align closely with your production objectives. This approach will help ensure a more efficient and dependable manufacturing process.
What sensors are most important for controlling cultivated meat bioprocesses?
To keep cultivated meat production on track, certain sensors play a critical role in monitoring and controlling the process. These include sensors for pH, dissolved oxygen, temperature, and metabolites like glucose and lactic acid.
- pH sensors: These are essential for maintaining the precise pH range that cell cultures need to thrive. Any deviation can disrupt the entire process.
- Oxygen and temperature sensors: These ensure the growth conditions remain ideal, supporting cell development and viability.
- Metabolite sensors: By tracking nutrient consumption, such as glucose levels or lactic acid build-up, these sensors allow for fine-tuned adjustments to the bioprocess.
By working together, these sensors enable real-time monitoring and control, ensuring consistent production and high-quality results.
How difficult is it to integrate new automation into an existing facility?
Integrating automation into an existing cultivated meat facility might seem daunting, but with careful planning, it’s entirely possible. The process typically involves retrofitting existing equipment, ensuring that new systems are compatible with the current setup, and providing comprehensive staff training to manage the updated workflows.
Thanks to advancements in bioprocess control software and sensors, real-time monitoring and automation of critical parameters - such as pH levels and nutrient concentrations - are now more accessible. These tools not only streamline operations but also enhance scalability, consistency, and efficiency, making automation a smart investment for optimising production processes.











